We talk about Nepal’s economy and Nepal’s economic status in this article. We will read about the economic development of Nepal. Nepal is a land-locked country as India and China surround it. It is also a developing country. The economic condition of Nepal is not that much better due to different political instability and many other reasons that may affect the development of the country.
Economic development in Nepal has been intricate and affected by the consistent trade in political scenarios, which has ranged from monarchy to being dominated by the Communist birthday celebration in the existing context. Nepal’s financial system lacks the entrepreneurial dynamism wished for more desirable monetary growth and long-term development. Overall, susceptible reform efforts have failed to stimulate broad-based poverty reduction.
Table of Contents
The country continues to hinder private-sector development, and political instability similarly weakens the ability to implement monetary reform or create a secure development environment. The statist strategy for economic administration and improvement has severely affected enterprise activity. Lack of transparency, corruption, and a burdensome approval method obstruct the much-needed expansion of private funding and production. Property rights are undermined with the aid of the inefficient judicial system, a situation of giant corruption and political influence.

How is Nepal Economy?
As we know, if the country has poor economic conditions, then there may arise many difficulties in the development programs, which won’t let the country move forward. So, for better development of the country, there is a need for better economic development, or we can say there must be sound economic conditions. The country has made much more progress toward sustainable economic growth since the 1950s. It has opened the country to economic liberalization, which has led to economic growth and improved living standards compared to the past. The biggest challenges the country faces in achieving higher economic development are the frequent changes in political leadership and corruption.
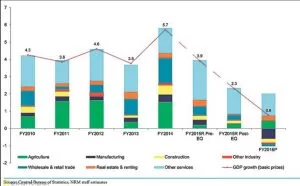
Nepal uses a series of five-year plans to make progress in economic development. Agriculture has become Nepal’s principal economic activity, employing about 65% of the population and providing 31.7% of GDP. Only about 20% of the total area is cultivable, while another 40.7% is forested, covered by shrubs, pastureland & forest, whereas the rest is primarily mountainous.
Economic Development of Nepal
The GDP of a country highly depends upon the remittances of foreign workers. According to statistics, the GDP of Nepal in 2014 was $67 billion, and the GDP growth according to 2020 was 7.5%. The GDP per capita is $2400. The different GDPs occupied by different sectors are agriculture at 35%, industry at 20%, and service at 45%. About 25.2% of the population is under the poverty line, according to statistics in 2010. The primary industries for earning are tourism, garments, food, beverages, metal manufacturing, herbs and so on.
According to the fiscal year 2013, there are $6 billion in revenues and $7 billion in expenses. The Cost of Living Index in Nepal is comparatively lower than in many countries, but not least. The quality of life has declined to a much less desirable value in recent years. Nepal was ranked 54th worst of 81 ranked countries. Nepal’s current score of 19.5 is better than in 2010 and much improved than its score of 27.5 in 1990. According to the present context, there are more expenses than revenue, which has been affecting the economic condition of Nepal.
Economy of Nepal Overview
In a very broad sense, the economy generally refers to something pecuniary and lucrative. When we refer to the economy of a country, it means the system of trade and industry by which wealth is made and used, and it encompasses the total resources of a country. The economy is affected by various processes and factors like culture, law, history, geography, etc of the country. These factors govern the functioning of the economy. The economy coexists with human practices and transactions. The economy of Nepal is not satisfactory. Let’s start with what the economy includes and how we can describe the economy of Nepal.
The economy can be of different types. It may be a market-based economy, command-based economy, or green economy. The economy of a country can be measured in various ways. However, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the favored method for its measurement. GDP provides the best general overview of the country’s economy. It is one of the primary indicators that represent the monetary value of goods produced in a country over a specific time period. The expression of GDP is usually in comparison to the previous year.

Talking about Nepal’s economy’s status quo, it is not in good nick. Sandwiched between two domineering neighboring countries, India and China, Nepal is a country that is still in an early developing phase. Nepal is a poor country, and among the South Asian countries, it is the poorest. Nepal centers on the rural economy, and there are many reasons for Nepal’s economy not to take a fast pace in development.
The main reason is political instability and corruption. The country’s political system has changed from a monarchy to being ruled by the Communist Party presently. The changes in the political scenario with rampant corruption are significant problems for Nepal’s economy to lagging. Also, Nepal lacks entrepreneurial dynamism. There is a lack of transparency.
Nepal’s GDP per capita is not satisfactory.
The statistics of Nepal‘s economy are not satisfactory. According to the data of 2014 estimation, GDP is $67 billion, and the GDP per capita is $2400. GDP’s composition according to the sector shows that agriculture includes 37%, industry entails 17%, and service includes 50%. GDP- real growth rate is 2.5% (2016). According to data from 2011, 23.8% of the total population is below the poverty line. The situation is appalling, as nearly a quarter of the total population of Nepal is impoverished. The household composition or income ranges from 3.2% in the lowest 10% to 29.8% in the highest 10%. 2012 estimations show the unemployment rate to be 38%.

Each year, youths join the rank of job seekers. Many strive to go abroad as unskilled labor or languish as a part of the unproductive workforce. The remittances form a significant part of the country’s economy. This unemployment rate creates a sense of vulnerability, hopelessness, and helplessness among the youth. Among the 4 million labor force, 81% are in agriculture, 16% in service and 3% in industry.
Nepal economy overview along with Nepal Import and Nepal Export
In a country with an agricultural economy, the other economic activities are manufacturing, trade, and tourism. About 81% of people are engaged in farming. The agricultural products produced in the country are rice, maize, wheat, sugarcane, root crops, etc. Only about 20% of the country’s total area can be cultivated. Forests, shrubs, and pasturelands cover 40%. The lowland Terai produces a surplus in agriculture, part of which is supplied in the hilly region of the country.

Manufacturing is in an early developmental stage and has a small part in the country’s GDP. Nepal exports commodities like carpets, clothing, leather goods, jute goods, etc., to its export partners, mainly India, the US, and Germany. The exports figure around $568 million (2002 est).
Nepal imports vast commodities like gold, machinery and equipment, petroleum products, and fertilizers, and the imports figure around $1.419 billion (2002 est). Tourism and remittances have been significant to Nepal’s economy. Nepal has 42,133 MW of technically viable hydroelectricity potential, but only a scintilla of it is installed at present, i.e., 730.47 MW.
Why is it challenging to raise the economy of Nepal?
Nepal’s economy after the earthquake
The earthquake of April 2015 created a huge loss in Nepal, and it affected the country’s economy as well. However, though at a slow pace, the country is heading back to the avenue of development. Considering the main hurdles to economic development, different plans must be made to nullify them. Nepal receives a huge amount of foreign aid for development projects. This should be used wisely for the long-term economic development of the nation.
Poverty in Nepal
Poverty in Nepal has always been one of the topics of discussion. Whenever we talk about a country, its economic condition is enjoined. We cannot avoid that Nepal is a poor country economically, though we have plenty of rich natural beauty to boast about. When we talk about poverty in Nepal, we are talking about the economic condition in the country that does not seem to be improving. Even though there is a slight improvement when comparing the yearly statistics, the result is ineffective. It shows that there are still a lot of people who are not able to meet their basic needs on a daily basis.
Poverty in Nepal has been a common phenomenon. The extent of commonness is such that whenever you browse the internet for information on our country, you will always come up with the line, “Nepal is a poor country.” Though this is bitter information for us, it is supported by the statistics also. The definition of poverty is highly variable. Different countries have different ways of interpreting poverty in their country using different dimensions.

In Nepal, earning less than 1 US dollar daily is considered poor. This is the poverty threshold or poverty line or poverty limit for Nepal. While talking about poverty, poverty may refer to absolute or relative poverty. But, in Nepal, relative poverty is not realized at all. The poverty line in Nepal refers to absolute poverty, which indicates the inability to maintain the minimum resources for physical health and efficiency.
Nepal was an isolated and agrarian society until the mid-20th century. Since the 1950s, the country has been going towards the path of economic development. However, agriculture remains the main occupation of the people even now. According to the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) fact book, we can see that the country has been going through some economic development since 1995. According to its statistics, the percentage of people falling below the poverty line in Nepal in 1995, 2003, 2004, 2008 and 2011 are 42, 31, 30.9, 24.7 and 25.2, respectively. These figures show that the country has been able to alleviate some of the problems of poverty in Nepal.

According to the latest data from the Asian Development Bank 2020, 25.2% of the people live below the national poverty line, and the proportion of the employed population below $1.90 purchasing power parity a day is 12.5%. The situation worsened after the earthquake in 2015. The devastating earthquake has made the prospect of economic growth in Nepal bleaker. The post-disaster need assessment report showed that there had been a lowering of GDP and income distress among the people. Also, the Indian embargo after the earthquake caused a reduction in imports and exports.
The economy of Nepal is Agriculture and Remittances.
Currently, the economy of Nepal is highly dependent on agriculture. Remittances have also been a significant part of the country’s GDP. However, various kinds of industries should also flourish for the economic development and sustainability of the country. Various causes have brought about poverty in Nepal. One of the most prominent problems is a high rate of population growth but low economic progress. Unemployment is the next problem, due to which the trend of brain drain has become rampant. Corruption is rampant as well, which has created a halt in the country’s economic growth, thus leaving the countrymen under the poverty line.
Alleviation of poverty in the country should be done systematically. Poverty should be taken as a political issue, and measures should be taken to alleviate it. Several alleviation approaches have been taken, but with the unstable and murky political situation in Nepal, the approaches have not become effective.
Alleviating poverty is not a simple task. It takes staggering efforts from all levels. Thus, with its transparent leadership, the government should take active measures to reduce the population below the poverty line in Nepal. The top political leaders of Nepal must pay attention to it.
